Co-authored by Christine McMonigal
By now you’ve probably heard of the myriad benefits that come from infrastructure modernization, including server consolidation. The cost savings on hardware, maintenance, and power and cooling systems alone make consolidation an appealing choice.
With fewer physical servers, data centers require less physical space. You’ll need a smaller area in the data center to host the servers, which means a corresponding decrease in demand on power and cooling infrastructure, and less resources required for management and troubleshooting. Your system would be more performant and efficient, enhancing your competitive edge. Pair all that with a significant reduction in carbon footprint and server consolidation is a no-brainer.
But let’s talk about performance. Can fewer servers really do the same amount of work?
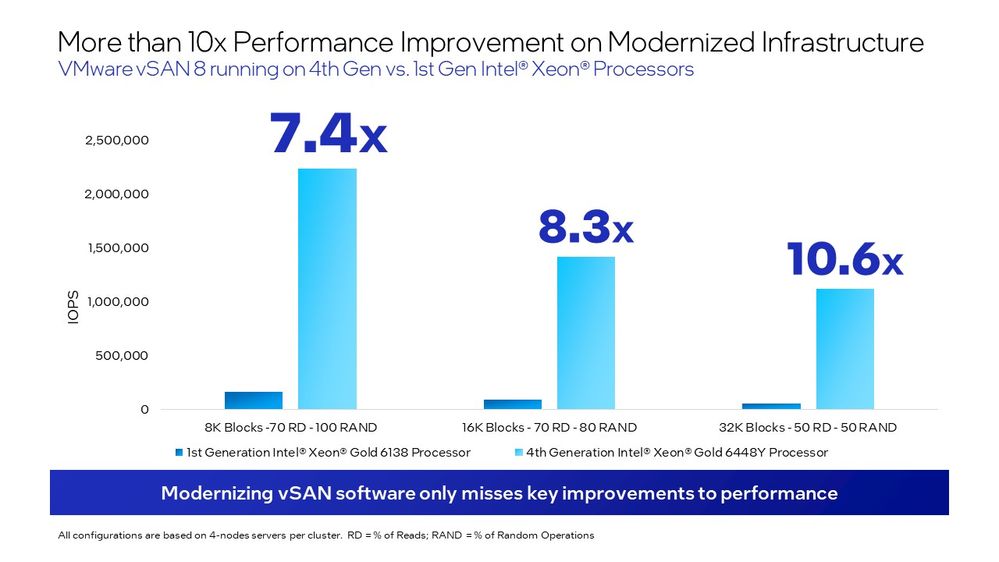
We recently put this to the test using VMware vSAN 8 ESA (Express Storage Architecture) on 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors with 4 nodes to compare the HCI Bench throughput to vSAN OSA (Original Storage Architecture) on 1st Gen Xeon processors with 4 nodes. Not only did we find higher throughput, but the numbers blew us away:
- 7.4x improvement in 8K block size-70% read data –100% random, simulating a typical noSQL workload running on vSAN
- 8.3x improvement in 16K block size-70% read data – 80% random, simulating a typical file systems workload
- 10.6x improvement in 32K block size-50% read data –50% random, simulating a typical SQL database workload running on vSAN
Our testing shows that by consolidating your servers, not only will you lower your operational costs with less hardware to maintain and less of a demand for space and energy, but you will get over 7.4x improvement in performance. In this case, less really is more – so much more!
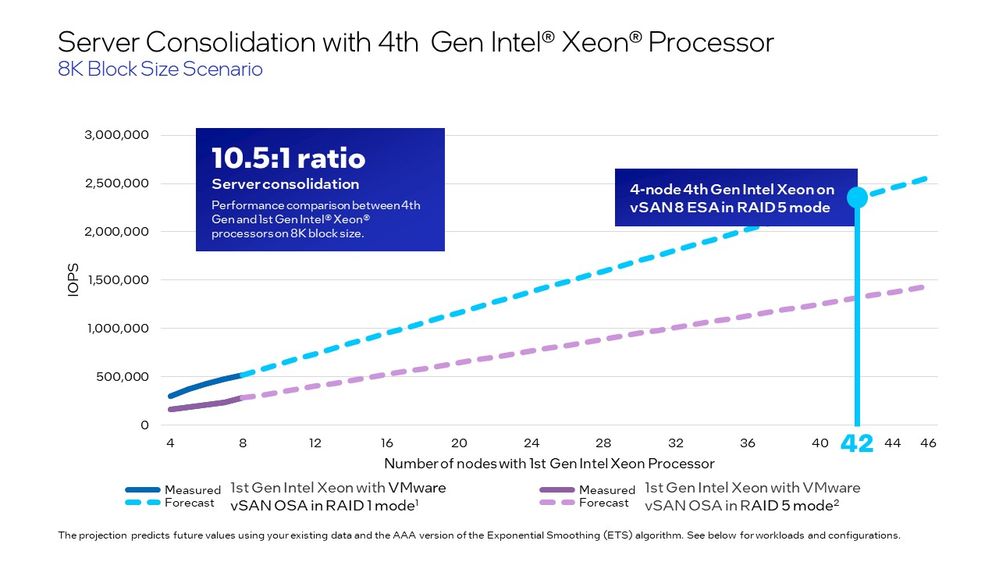
To take this a step further, we wanted to see how many servers with the 1st gen processors it would take to reach the performance of one 4node cluster featuring 4th gen processors. To do so we tested scale-out approach for the older vSAN OSA cluster on 1st generation Xeon from 4 to 8 nodes and then used that data to project out the performance of the cluster with even more nodes using the ETS (Exponential Smoothing) algorithm.
Our calculations showed that it would take a projected 42 nodes with 1st generation Intel Xeon Scalable processors to reach the performance of 4 nodes with the 4th generation. Though it is unrealistic to test 42 nodes for hard data, this projection shows a 10.5:1 ratio in performance enhancement. This means that by modernizing you could have one new server that can do the work of ten old servers. Think of what you could do with all the space, time, and resources you’ll save.
It’s hard to ignore the numbers. Of course, your consolidation ratio will vary with the workloads running on your vSAN clusters, but server modernization and consolidation with VMware vSAN 8 and 4th Gen Intel Xeon processors is the smart move all around. To learn more, email patryk.wolsza@intel.com.
Workloads and Configurations
Intel Xeon Gold 6138 – RAID-5: Test by Intel as of 01/06/23. 4- to 8-node clusters, 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6138 CPU @ 2.00GHz, 20 cores, HT On, Turbo On, Total Memory 384GB (12x32GB DDR4 2666 MT/s [2666 MT/s]), BIOS 2.17.1, microcode 0x2006e05, 2x I350 Gigabit Network Connection, 2x Ethernet Controller X710 for 10GbE SFP+, 2x 349.3G INTEL MDTPE21K375GA, 6x 1.8T INTEL SSDPE2KX020T8, OS/Software: VMware 7.0U3G, 20328353, vSAN OSA – default policy (RAID5, 2DG), using HCI Bench 2.8, FIO3.3. Throughput test 8k profile (I/O size 8k, Read percentage 70%, Random percentage 100%, latency target mode<10ms, #VMs per cluster 16, vCPU 4, vRAM 8, # data disks per VM 4, size of disk 50GB).
Intel Xeon Gold 6138 – RAID-1: Test by Intel as of 01/06/23. 4- to 8-node clusters, 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6138 CPU @ 2.00GHz, 20 cores, HT On, Turbo On, Total Memory 384GB (12x32GB DDR4 2666 MT/s [2666 MT/s]), BIOS 2.17.1, microcode 0x2006e05, 2x I350 Gigabit Network Connection, 2x Ethernet Controller X710 for 10GbE SFP+, 2x 349.3G INTEL MDTPE21K375GA, 6x 1.8T INTEL SSDPE2KX020T8, OS/Software: VMware 7.0U3G, 20328353, vSAN OSA – default policy (RAID-1, 2DG), using HCI Bench 2.8, FIO3.3. Throughput test 8k profile (I/O size 8k, Read percentage 70%, Random percentage 100%, latency target mode<10ms, #VMs per cluster 16, vCPU 4, vRAM 8, # data disks per VM 4, size of disk 50GB).
Intel Xeon Gold 6448Y: Test by Intel as of 08/25/23 4-node cluster, 2x Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6448Y, 32 cores, HT On, Turbo On, NUMA 2, Integrated Accelerators Available [used]: DLB 0 [0], DSA 2 [0], IAA 0 [0], QAT 0 [0], Total Memory 512GB (16x32GB DDR5 4800 MT/s [4800 MT/s]), BIOS SE5C741.86B.01.01.0004.2303280404, microcode 0x2b0001b0, 2x Ethernet Controller E810-C for QSFP, 9x 3.5T INTEL SSDPF2KX038TZ, 2x 223.6G INTEL SSDSCKKB240GZ, OS/Software: VMware 8.0.1, 21495797, vSAN ESA – Optimal default policy (RAID-5, flat), using HCI Bench 2.8, FIO3.3. Throughput test 8k profile (I/O size 8k, Read percentage 70%, Random percentage 100%, latency target mode<10ms, #VMs per cluster 16, vCPU 4, vRAM 8, # data disks per VM 4, size of disk 50GB).
Notices and Disclaimers
Performance varies by use, configuration and other factors. Learn more at www.Intel.com/PerformanceIndex.
Performance results are based on testing as of dates shown in configurations and may not reflect all publicly available updates. See backup for configuration details. No product or component can be absolutely secure.
Your costs and results may vary.
Intel technologies may require enabled hardware, software or service activation.
 Patryk is a vExpert and Cloud Solutions Architect in Intel Datacenter & AI Group, with a focus on Software Defined Infrastructure. With more than a decade of expertise in different cloud platforms, Patryk has broad experience in cloud solutions, influencing data center designs, and understanding connections between ordinary Data Centers, virtualization, SDI, cloud, and edge. His recent focus is on optimization workloads leveraging differentiation features and building technology-enabling stacks.
Patryk is a vExpert and Cloud Solutions Architect in Intel Datacenter & AI Group, with a focus on Software Defined Infrastructure. With more than a decade of expertise in different cloud platforms, Patryk has broad experience in cloud solutions, influencing data center designs, and understanding connections between ordinary Data Centers, virtualization, SDI, cloud, and edge. His recent focus is on optimization workloads leveraging differentiation features and building technology-enabling stacks.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.